Users have a lot to worry about when downloading and playing media files. Are the files legal? Can their computers play the required file formats? Now there’s yet another problem to add to the list: Will a media file try to install spyware?
When Windows Media Player encounters a file with certain “rights management” features enabled, it opens the web page specified by the file’s creator. This page is intended to help a content providers promote its products — perhaps other music by the same artist or label. However, the specified web page can show deceptive messages, including pop-ups that try to install software on users’ PCs. User with all the latest updates (Windows XP Service Pack 2 plus Windows Media Player 10) won’t get these popups. But with older software, confusing and misleading messages can trick users into installing software they don’t want and don’t need — potentially so many programs that otherwise-satisfactory computers become slow and unreliable.
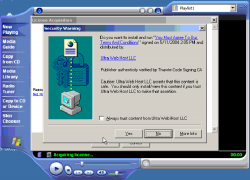 Screen-shot of the initial on-screen display. If users press Yes, scores of unwanted programs are installed onto their PCs.
Screen-shot of the initial on-screen display. If users press Yes, scores of unwanted programs are installed onto their PCs.
I recently tested a Windows Media video file, reportedly circulating through P2P networks, that displays a misleading pop-up which in turn attempts to install unwanted software onto users’ computers. I consider the installation misleading for at least three reasons.
- The pop-up fails to name the software to be installed or the company providing the software, and it fails to give even a general description of the function of the software.
- The pop-up claims “You must agree to our terms and conditions” — falsely suggesting that accepting the installation is necessary to view the requested Windows Media video. (It’s not.)
- Even when a user specifically requests more information about the program to be installed, the pop-up does not provide the requested information — not even in euphemisms or in provisions hidden mid-way through a long license. Clicking the pop-up’s hyperlink opens SpiderSearch’s Terms and Conditions — a page that mentions “receiving ads of adult nature” and that disclaims warranty over any third-party software “accessed in conjunction with or through” SpiderSearch, but that does not disclose installation of any third-party software.
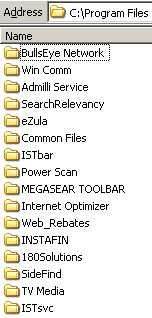 Screen-shot of my Program Files folder, showing some of the programs installed on my test computer.
Screen-shot of my Program Files folder, showing some of the programs installed on my test computer.
On a fresh test computer, I pressed Yes once to allow the installation. My computer quickly became contaminated with the most spyware programs I have ever received in a single sitting, including at least the following 31 programs: 180solutions, Addictive Technologies, AdMilli, BargainBuddy, begin2search, BookedSpace, BullsEye, CoolWebSearch, DealHelper, DyFuca, EliteBar, Elitum, Ezula, Favoriteman, HotSearchBar, I-Lookup, Instafin, Internet Optimizer, ISTbar, Megasearch, PowerScan, ShopAtHome Select, SearchRelevancy, SideFind, TargetSavers, TrafficHog, TV Media, WebRebates, WindUpdates, Winpup32, and VX2 (Direct Revenue). (Most product names are as detected by Lavasoft Ad-Aware.) All told, the infection added 58 folders, 786 files, and an incredible 11,915 registry entries to my test computer. Not one of these programs had showed me any license agreement, nor had I consented to their installation on my computer.
I retained video, packet log, registry, and file system logs of what occurred. As in my prior video of spyware installing through security holes, my records make it possible to track down who’s behind the installations — just follow the money trail, as captured by the “partner IDs” within the various software installation procedures. When one program installs another, the second generally pays the first a commission, using a partner ID number to track who to pay. These numbers make it possible to figure out who’s profiting from the unwanted installations and, ultimately, where the money is going.
Figuring Out Who’s Responsible
Most directly responsible for this mess is ProtectedMedia — the company that caused my computer to display the initial misleading pop-up shown above. ProtectedMedia invited the installation of some unwanted programs, which in turn installed others, but ProtectedMedia could readily stop these behaviors, e.g. by disabling its misleading pop-up installation attempts.
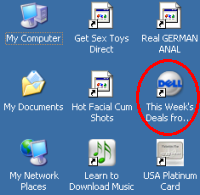 Screen-shot of the icons added to my test computer’s desktop. Note a new link to Dell — an affiliate link such that Dell pays commissions when users make purchases after clicking through this link.
Screen-shot of the icons added to my test computer’s desktop. Note a new link to Dell — an affiliate link such that Dell pays commissions when users make purchases after clicking through this link.
But who pays ProtectedMedia? As I started to follow the money trail, I was surprised to see that some of the unrequested programs receive funds from respected online merchants. Several of the spyware installations added new toolbars to my computer’s browser and new icons to my desktop. If users click through these links, then make purchases from the specified merchants, the merchants pay commission to the affiliates who placed these toolbars and icons on users’ PCs. Even large, otherwise-reputable companies pay commissions through these systems, thereby funding those who install unwanted software on users’ computers. In my testing, I received affiliate links to Amazon, Dell, Hotwire, Match.com, Travelocity, and others. Many of these links pass through affiliate tracking networks LinkShare and Commission Junction.
Of course, these merchants may not have intended to support spyware developers. For example, merchants may have approved the affiliates without taking time to investigate the affiliates’ practices, or the affiliates’ actions may be unauthorized by the merchants. (That’s what Dell said when I previously found Dell ads running on Claria.) In future work, I’ll look in greater detail at which merchants pay affiliate commissions to which spyware programs, and I’ll also further document which merchants purchase advertising from companies whose software sneaks onto users’ computers.
Other companies partially responsible for these practices are the providers of the unwanted software — companies that pay commissions to distributors foisting their software onto users’ computers. In general there’s no reason to expect honorable behavior by providers of unwanted software. But some of the programs I received come from big companies with major investment backing: 180solutions received $40 million from Spectrum Equity Investors; Direct Revenue received $20 million from Insight Venture Partners; and eXact Advertising (makers of BargainBuddy and BullsEye) received $15 million from Technology Investment Capital Corp. With so much cash on hand, these companies are far from judgment-proof. Why are they paying distributors to install their software on users’ computers without notice and consent?
The problematic installations ultimately result from the “feature” of Windows Media Player that lets media files open web pages. But most users will only receive the contaminated files if they download files from P2P filesharing networks. Of course, rogue media files are but one way that P2P networks spread spyware. For example, users requesting Kazaa receive a large bundle of software (including Claria’s GAIN), after poor disclosures that bury key terms within lengthy licenses, without even section headers to help readers find what’s where. Users requesting Grokster receive unwanted software even if they press Cancel to decline Grokster’s installation (details).
Ed Bott offers an interesting, if slightly different, interpretation of these installations. Ed rightly notes that users with all the latest software — not just Windows XP Service Pack 2, but also Windows Media Player 10 — won’t get the tricky pop-ups described above. Ed also points out that Windows Media Player displays of ActiveX installation prompt pop-ups are similar to deceptive methods users have seen before, i.e. when web sites try to trick users into installing software. True. But I think Ed gives too little weight to the especially deceptive circumstances of a software installation prompt shown when users try to watch a video. For one, legitimate media players actually do use these prompts to install necessary updates (i.e. the latest version of Macromedia Flash), and Windows Media Player often shows similar prompts when it needs new codecs or other upgrades. In addition, the unusually misleading (purported) product name and company name make it particularly easy to be led astray here. Users deserve better.
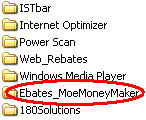 Partial screen-shot taken from video of Ebates installation through a security hole, without any notice or consent.
Partial screen-shot taken from video of Ebates installation through a security hole, without any notice or consent.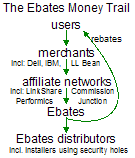 The Ebates Money trail: users -> merchants -> affiliate networks -> Ebates -> Ebates distributors
The Ebates Money trail: users -> merchants -> affiliate networks -> Ebates -> Ebates distributors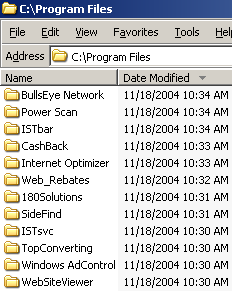 Malware installed through a single security exploit
Malware installed through a single security exploit